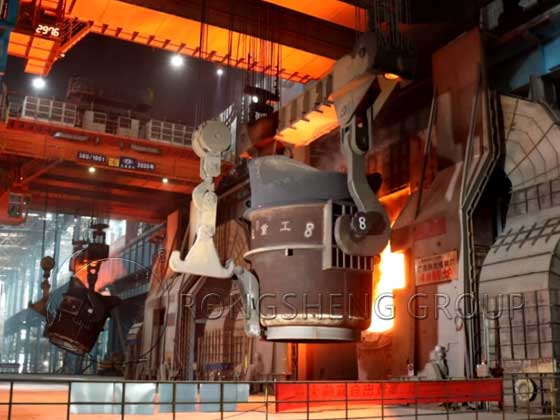
The hazards of magnesia-chrome waste bricks. Cr in magnesia chrome bricks has many beneficial effects. However, under high temperatures, and alkaline and oxidizing atmospheres, some chromium will be converted into water-soluble hexavalent chromium, causing serious harm. Cr+ is highly harmful to human skin and mucous membranes. It can cause papules, ulcers, nasal septum perforation, and respiratory inflammation. It can also cause skin cancer and lung cancer. For example, the risk of lung cancer among workers working with chromic acid and chromium-containing pigments is 10 to 30 times higher than that of the general population.
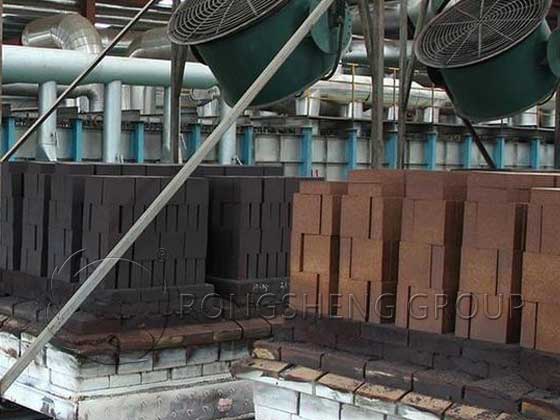

In cement rotary kilns, the areas where refractory materials corrode the fastest are mainly the fire point at 9.5~16m and the location without kiln skin at 27~33m. However, the waste bricks dismantled from 3~9.5m and 16~25m are the ones that emit the most Cr+. The Cr+ carried by these two parts of waste bricks accounts for 92% of the total discharged hexavalent chromium, while the Cr+ discharged from other parts only accounts for 8%.
A 4000t/d cement kiln dismantles 181t of magnesia-chrome bricks at one time, and the waste bricks carry an average of Cr+183kg. The average Cr6+ content is about 1kg/t or 1000mg/kg, which is 20,000 times higher than the Cr6+ content of 0.05 mg/L allowed by national environmental standards for Level IV. Therefore, a single discharge of magnesia-chromium bricks can harm 3.6 million tons of pure water. In other words, 2.5 tons of water will be harmed for every 1 ton of clinker produced! It can be seen that the harm of magnesia-chrome waste bricks to the environment and the threat to human health are very alarming.
It is very unreasonable to use magnesia chrome bricks in the 3~9m and 27~33m sections in the cement rotary kiln. At a position 3 to 9 meters inside the kiln, close to the kiln entrance, the oxygen partial pressure is high. The chromium in the magnesia-chromium bricks is easily oxidized, causing the fire bricks to contain high hexavalent chromium, which seriously harms the environment. At 27~33m in the kiln, the hot end temperature and alkali content in the transition zone are very high. Cr in magnesia-chrome bricks is easily converted into K2CrO4 and volatilizes, causing the magnesia-chrome bricks to corrode quickly. Therefore, magnesia-chrome bricks are only used in the most severely corroded parts 9.5 to 16 meters inside the kiln, and chromium-free alkaline bricks can be used in other parts. In this way, it does not affect the life of the kiln lining and reduces the harm of waste bricks.
Suppression of the Hazards of Magnesia-Chrome Waste Bricks
After suppression treatment, the hexavalent chromium in the magnesia-chrome waste bricks can be destroyed, so that the waste bricks can meet the requirements for safe discharge. The most economical known inhibition method is thermal reduction inhibition – the waste bricks are buried in carbon and heat treated at 900~1000℃, and CO gas is used to reduce hexavalent chromium into non-toxic substances.
When treated at around 900°C, hexavalent chromium in waste bricks can be removed. Make the Cr6+ content of the immersion liquid <0.05mg/L, meeting the requirements of Class IV water stipulated in the national environmental standards. In the same way, firing in a weak reducing atmosphere before stopping the kiln will also help reduce the Cr6+ content in magnesia-chrome waste bricks.