Double-chamber kiln is widely used in the production of metallurgical lime due to its advantages such as low heat consumption, high degree of automation, easy-to-adjust production, parallel flow heat storage, less refractory material usage, less floor space, stable product quality, etc. A project uses this kiln to produce and supply light-burned dolomite. Rongsheng Refractory Material Manufacturer supplies refractory lining materials for double-chamber kiln double C structure kiln of light-burned dolomite.
Double-Chamber Kiln Refractory Lining Structure
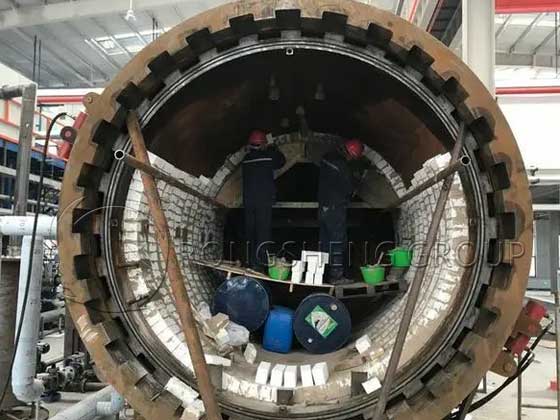
The construction of a double-chamber kiln of a light-burned dolomite manufacturer adopts a domestic double-chamber kiln with a “double C structure”. Its internal refractory masonry structure is shown in Figure 1. The double-chamber kiln lining structure is divided into cooling zone, calcining zone, and preheating zone from bottom to top. They are built with refractory materials with good high-temperature resistance, wear resistance, and thermal insulation performance. The two kiln chambers are constructed with an intermediate channel and 8 cooling pillars. The outer ring bricklayer of the kiln is counted from the bottom of the kiln chamber, a total of 194 layers.
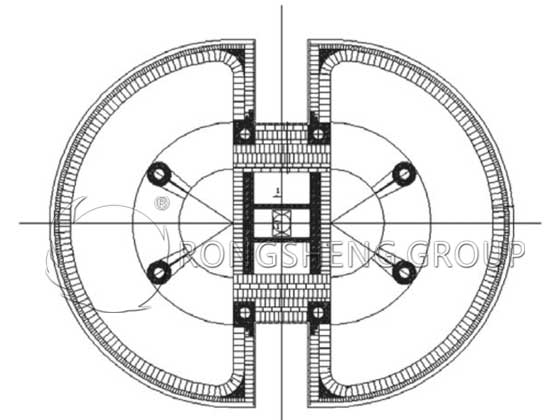
The cooling belt and the bottom of the steel structure are leveled with low cement castables, and then the cooling belt is laid. From the 1st to the 40th floor, from the steel shell structure outward, coating material, two layers of fiberboard, insulation bricks, and high-strength clay bricks are used in sequence. The thickness of the fiberboard is 30mm, the thickness of the insulation brick is 230mm, and the thickness of the high-strength clay brick is 260mm. When laying each layer of bricks, expansion joints are reserved in the circular ring of the kiln brick layer at a certain distance.
From the 41st to the 82nd floor, as the kiln height gradually approaches the calcining zone area, the working temperature increases accordingly, and the brick lining working layer is changed to high-alumina refractory bricks.
The middle channel is equipped with a fire door. It is used to observe the ash accumulation during the kiln shutdown, and a template is required during masonry.
The calcining zone has the highest temperature, which can reach 1100℃. Considering the calcination characteristics and temperature, the working layer of the 83rd to 161st layers of bricks on the outer ring of the kiln is built with mullite refractory bricks. From the steel shell structure to the outside, it is built with coating material, two layers of fiberboard, insulation bricks, and mullite bricks in sequence.
Anchors are welded on the bottom of the steel structure and the supporting structure inside the kiln, and castables are used for masonry. At the same time, thermocouples are evenly arranged in the inner and outer ring areas of each kiln chamber to detect the calcination of the kiln.
The 162nd to 194th brick lining working layer is built with high-strength clay bricks as part of the preheating zone.
The entire kiln structure should be strictly symmetrical. In order to ensure the construction period, the masonry of the two kiln chambers can be carried out at the same time. During the masonry process, overlapping of brick joints should be avoided, and the mortar should be applied in sufficient and uniform amounts.
Problems with the Lining of the Double-C Structure Lime Kiln
After the double C structure lime kiln was in production for a period of time, two high-temperature spots were found on the surface of the furnace shell, and it was forced to be emptied for inspection. It was found that the refractory bricks in the working layer at about 700mm from the bottom of the kiln spray gun were burned, and the refractory bricks in the insulation layer were molten (see Figure 2). In order to avoid the recurrence of this phenomenon, it is necessary to analyze the cause of the burning of refractory bricks. The project team conducted a comprehensive analysis of the aspects of design, process operation, raw material structure, equipment installation structure, etc. Find the cause and optimize and rectify it.
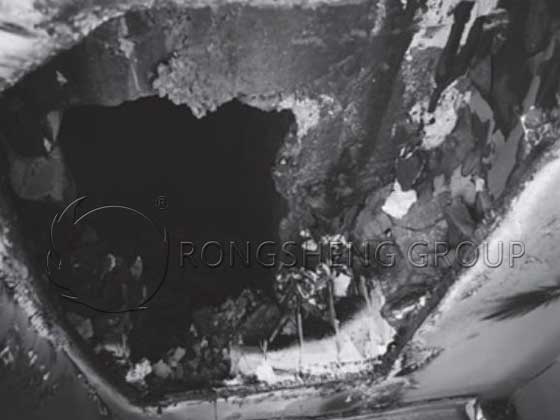

After investigation and inspection, it was found that the coal powder spraying gun was not installed correctly, and the flame directly washed the furnace wall, which was the direct cause of the burning of the refractory materials. The coal powder conveying fan was not a variable frequency fan, the wind pressure was too high, and the flow rate was too fast. The coal powder guide pipe was worn in less than one month, and the coal powder conveying of the spray gun increased, which was another reason for the aggravation of the burning of the refractory materials.
Rectification of the Lining of the Double-C Structure Lime Kiln
The construction and maintenance team was required to strictly follow the drawings to ensure that the spray gun was vertically parallel and downward and to ensure the distance between the spray gun and the furnace wall. This reduced the burning of refractory materials.
At the same time, the pulverized coal conveying fan was retrofitted with frequency conversion, and the fan operation program was updated. That is, the fan operating frequency was reduced during the reversing period, and the fan speed was adjusted according to the kiln conditions during the combustion period. This ensured the transportation of pulverized coal while reducing power consumption. The double-chamber kiln after the rectification had a good operating effect, and no corresponding refractory material burning occurred.
How to Improve the Service Life of the Kiln Refractory Lining?
After the double C structure kiln refractory bricks were overhauled and the conveying fan frequency conversion was modified, the entire kiln no longer had refractory material burning. This fully proves that the rectification effect is good.
- (1) The abnormal damage of the furnace wall in the high-temperature section of the lime kiln causes the furnace shell to turn red. The main reason is that the mullite bricks in the working layer are corroded and melted at high temperatures during the production process.
- (2) Alkali metals such as K₂O and Na₂O react with mullite bricks at high temperatures to form low-melting products such as feldspar. The mullite bricks are continuously corroded, and the furnace wall becomes thinner after melting, which causes the furnace shell to turn red at high temperatures.
- (3) The source of alkali metal oxides in the lime kiln is mainly the ash of the mixed coal. Due to the double C structure of the kiln type, abnormal installation of the spray gun will also cause ash to adhere near the end wall and corrode the furnace wall.
- (4) The frequency conversion of the conveying fan is conducive to reducing power consumption, stabilizing the kiln condition, reducing the erosion of the coal powder guide pipe, and increasing its service life.
Rongsheng Refractory Material Production and Sales Manufacturers is a powerful refractory material production and sales manufacturer. Rongsheng Refractory Manufacturer can customize the construction and maintenance plan of refractory lining according to the actual working conditions of high-temperature industrial furnaces. For high-quality refractory bricks and amorphous refractory products, contact us for free samples and quotes.














